Platform Lifts and Accessible Routes
Posted on - Tuesday, June 4th, 2019Connection Between Levels
The ADA requires that different levels and floors within a facility be connected by an accessible route. An accessible route is a continuous and unobstructed way to travel from any point in a building or facility. Some ways to achieve an accessible route is through ramps or elevators. A method that is confusing is the use of a platform lift, wheelchair lift or chair lift. Those, even though they help to achieve access in some cases, are not always allowed as part of an accessible route. This newsletter will explain when they are allowed and when they are not.

Existing Buildings

New Construction
But in new construction projects, you are only allowed the use of platform lifts in certain situations. Here are the only circumstances where you can use them as part of an accessible route:
206.7.1 Performance Areas and Speakers’ Platforms
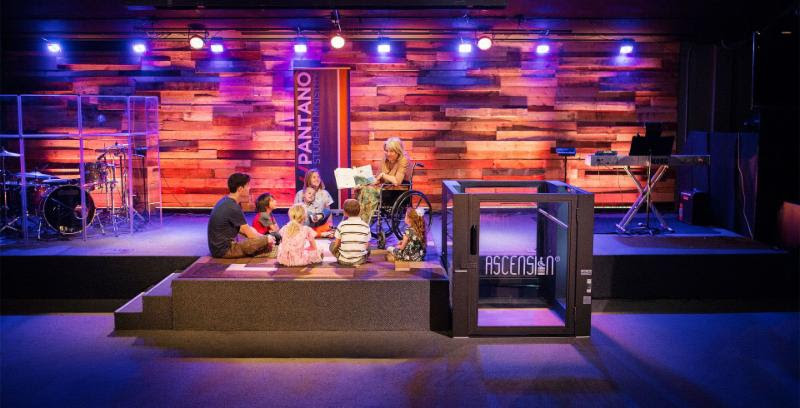

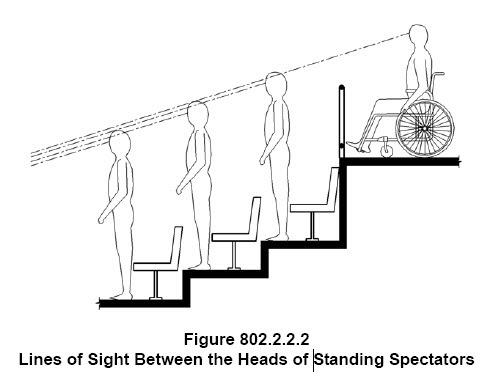
206.7.2 Wheelchair Spaces: Platform lifts shall be permitted to provide an accessible route to comply with the wheelchair space dispersion and line-of-sight requirements
206.7.3 Incidental Spaces which are not public use spaces and which are occupied by five persons maximum.
206.7.4 Judicial Spaces: Platform lifts shall be permitted to provide an accessible route to: jury boxes and witness stands; raised courtroom stations including, judges’ benches, clerks’ stations, bailiffs’ stations, deputy clerks’ stations, and court reporters’ stations; and to depressed areas such as the well of a court.
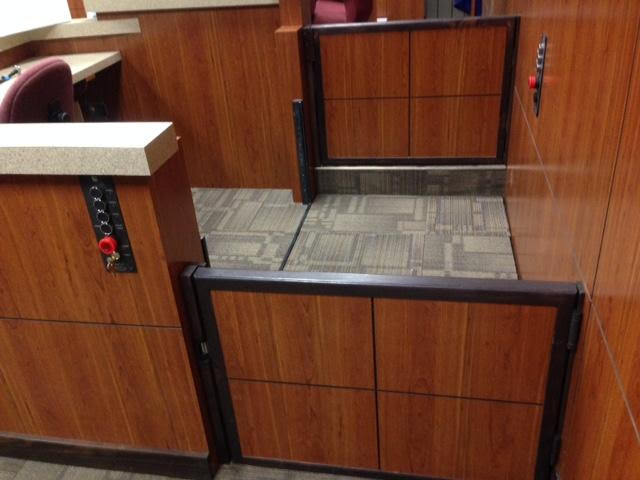

206.7.5 Existing Site Constraints: Platform lifts shall be permitted where existing exterior site constraints make use of a ramp or elevator technically infeasible.

When you see the word “technically infeasible”, you may need permission (variance) from the State agency with jurisdiction of the Standards
206.7.6 Guest Rooms and Residential Dwelling Units: Platform lifts shall be permitted to connect levels within transient lodging guest rooms required to provide mobility features or residential dwelling units required to provide mobility features

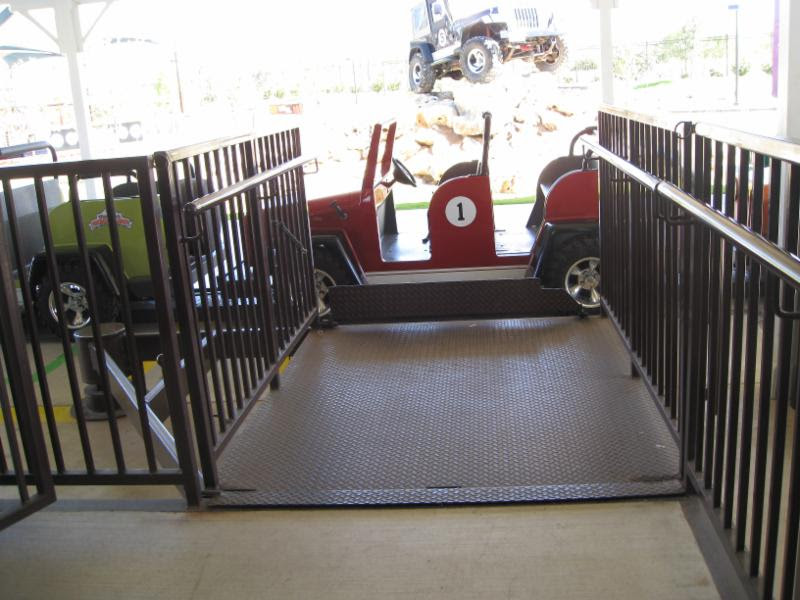
206.7.7 Amusement Rides. Platform lifts shall be permitted to provide accessible routes to load and unload areas serving amusement rides.

206.7.8 Play Areas. Platform lifts shall be permitted to provide accessible routes to play components or soft contained play structures.

206.7.9 Team or Player Seating. Platform lifts shall be permitted to provide accessible routes to team or player seating areas serving areas of sport activity.

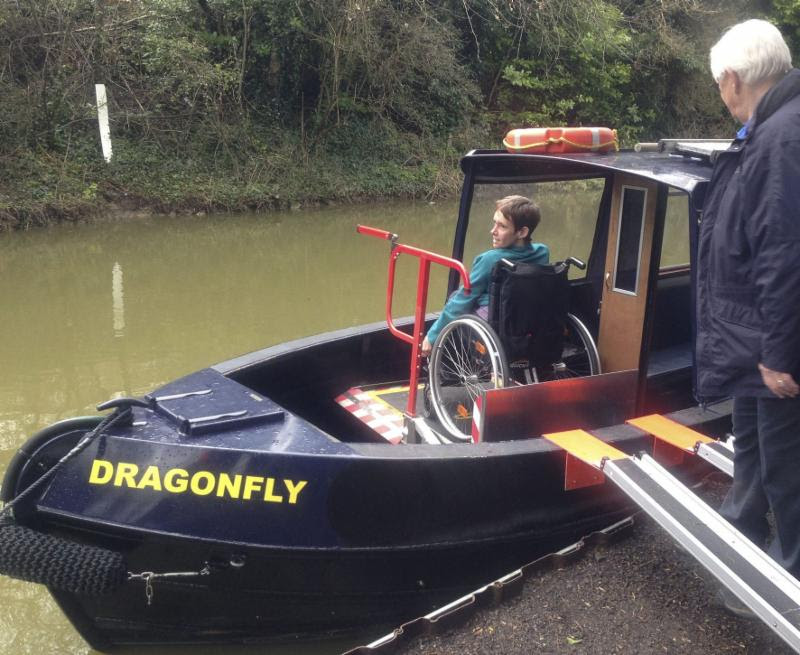
206.7.10 Recreational Boating Facilities and Fishing Piers and Platforms. Platform lifts shall be permitted to be used instead of gangways that are part of accessible routes serving recreational boating facilities and fishing piers and platforms.

And as part of an accessible means of egress as mentioned in 207.2
207.2 Platform Lifts. Standby power shall be provided for platform lifts permitted by section 1003.2.13.4 of the International Building Code (2000 edition and 2001 Supplement) or section 1007.5 of the International Building Code (2003 edition) (incorporated by reference, see “Referenced Standards” in Chapter 1) to serve as a part of an accessible means of egress
What constitutes a platform lift?
The scoping section of the 2010 ADA mentions platform lifts. But what about chair lifts? Are they allowed? what is the difference?
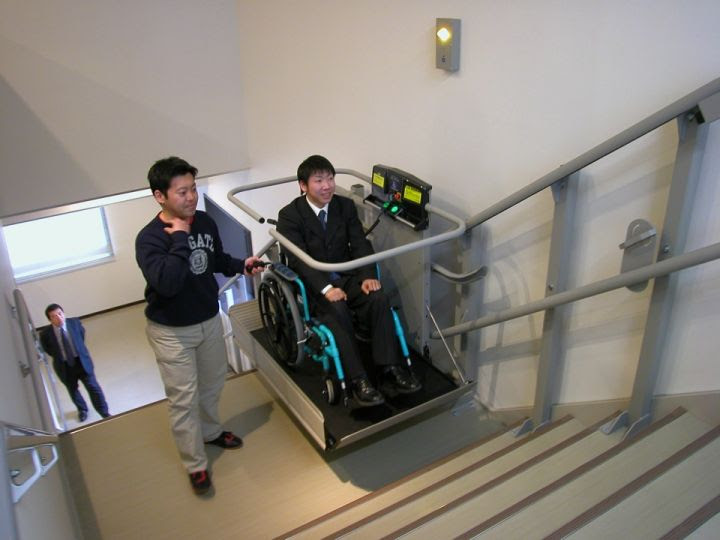

According to the technical standards 410
410.1 General. Platform lifts shall comply with ASME A18.1 (1999 edition or 2003 edition) (incorporated by reference, see “Referenced Standards” in Chapter 1). Platform lifts shall not be attendant-operated and shall provide unassisted entry and exit from the lift.
ASME A18.1-1999 and ASME A18.1-2003 address the design, construction, installation, operation, inspection, testing, maintenance and repair of lifts that are intended for transportation of persons with disabilities.
Lifts are classified as: vertical platform lifts, inclined platform lifts, inclined stairway chairlifts, private residence vertical platform lifts, private residence inclined platform lifts, and privateresidence inclined stairway chairlifts.
This document [The 2010 ADA Standards] does not permit the use of inclined stairway chairlifts which do not provide platforms because such lifts require the user to transfer to a seat.
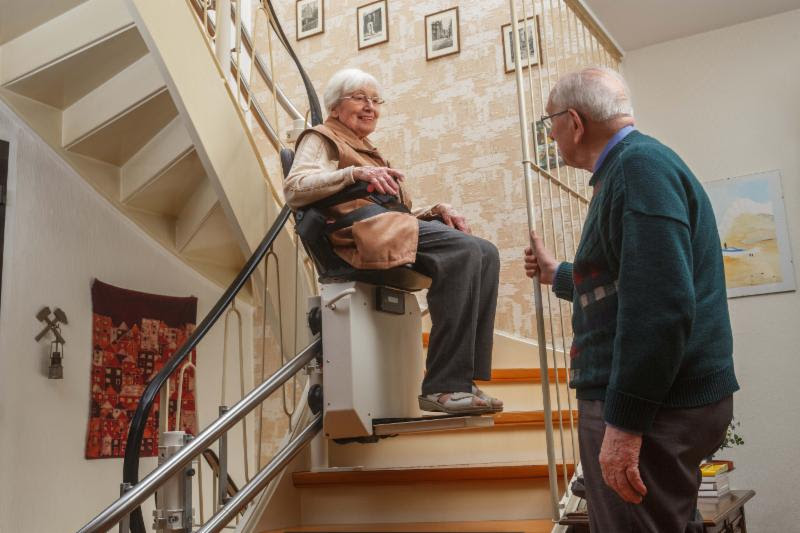

The advisory explains the different types:
Inclined stairway chairlifts and inclined and vertical platform lifts are
available for short-distance vertical transportation. Because an accessible route requires an 80 inch(2030 mm) vertical clearance, care should be taken in
selecting lifts as they may not be equally suitable for use by people using wheelchairs and people standing. If a lift does not provide 80 inch (2030 mm) vertical clearance, it cannot be considered part of an accessible route in new construction.
The ADA and other Federal civil rights laws require that accessible features be maintained in working order so that they are accessible to and usable by those people they are intended to benefit. Building owners are reminded that the ASME A18 Safety Standard for Platform Lifts and Stairway Chairlifts requires routine maintenance and inspections. Isolated or temporary interruptions in service due to maintenance or repairs may be unavoidable; however, failure to take prompt action to effect repairs could constitute a violation of Federal laws and these requirements.
In summary, if the inclined chair lift meets the requirements of the ASME A18.1 then they can be used instead of a platform lift where they are allowed.
 Abadi
Abadi 
